Configure native products
Product configuration has to do with setting up the technical aspects of your product. This includes configuring at least one version, setting up roles and permissions, using AI, deciding whether you want to implement data transfer, and making the product available for specific workspaces.
DevHub allows working on different aspects of product creation simultaneously. Still, you must complete both product details and configuration to onboard your product to Open OS successfully.
Leverage product versions
Product versions enable you to maintain isolated product configurations for the development and production environments in Open OS. You can support multiple different versions—each with its route, roles, permissions, and so on—as you continue to develop and test your product.
In the following sections, we'll look at these fields and parameters to give you a quick overview of the data you should have handy when onboarding products.
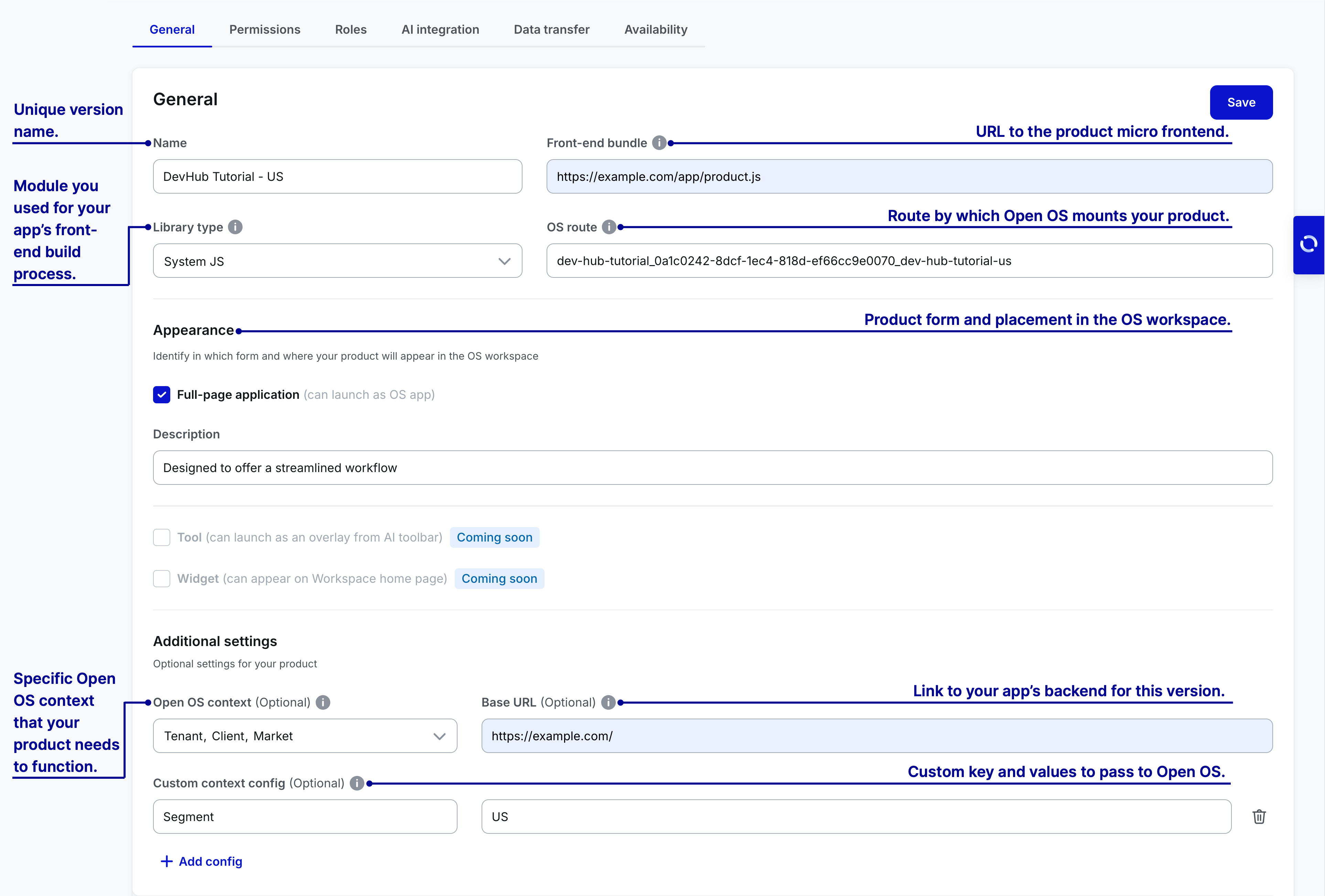
Configure general parameters
Each version configuration requires a basic set of parameters that define how your product will be mounted in Open OS. For successful product launch, make sure to fill out all of the required fields.
WPP AI Assistant contains pre-defined tools in the Quick Access toolbar. Selecting the Tool checkbox in general parameters makes the app available in WPP AI Assistant, allowing it to be added to the Quick Access toolbar and launched as an overlay.
Use a unique and self-explanatory version name. Whenever possible, link it to the product name. Follow the logic of examples:
| Product name | Version Name |
|---|---|
| Segment Opportunity Simulator | Segment Opportunity Simulator US, Segment Opportunity Simulator UK |
| Architect | Architect-Campaigns, Architect-Audiences, Architect-Touchpoints |
Because any version can serve as a standalone app, the appropriate version naming helps associate the version with the right product.
Open OS context
Open OS context is an optional field that allows you to specify what Open OS context your product needs to function properly. These context requirements also decide where your product can be located within the Open OS Navigation Tree and Orchestration.
Navigation Tree and Orchestration support three primary navigation structures:
-
Hierarchy. Reflects a predefined hierarchical order for navigation, traditionally presented as Client, Market, and Brand:
- Client—a specific client the agency works with, often an entity with sub-entities.
- Market—a country.
- Brand—a particular brand or other sub-entity under a Client.
The dynamic nature of hierarchy allows modifying this order, omitting certain levels, and adding new ones.
For example, suppose an agency exclusively works with one client. In that case, it can set this client as the top level of navigation, restructuring the rest of their workspace around specific markets and brands. Client would remain part of the hierarchy, even if not displayed, and can be used as a context variable for products.
-
Projects. Organizes navigation around the projects the agency is managing. This view intermingles products with custom workflows to cater to project-specific requirements.
-
Custom. Offers complete customization, allowing to combine static pages, hierarchies, projects, and products at any level within the navigation.
Regardless of the navigation setup for a given workspace, your product should be displayed at the expected level. Open OS achieves this by providing context variables for navigation, which you can specify in DevHub.
For example, if your product involves market research and requires country-specific data analysis, it wouldn't be necessary for it to exist on the Client or Brand levels. Thus, when onboarding your product, you'd need to identify "Market" as required Open OS context. Once you do that, Tenant Admins will be restricted to adding your products only on the Market level in navigation.
Alternatively, your product might operate independently from the Open OS navigation. In this case, you would leave the required Open OS context field empty, and Tenant Admins could place your product at any level within the hierarchy or outside of it.
Add roles and permissions
Open OS features a built-in authorization and permissions management module, Open Authorization, which allows you to control user access to different functions and data in your product. To onboard a product, you need to integrate with Open Authorization.
There are no specific requirements for this flow—add the roles and permissions, and then map them together in your preferred sequence. Note that permissions and roles are now optional for version activation on workspaces.
Take a look at our Auth, roles, and permissions docs for more context on Open Authorization.
Permissions
Permissions are individual sets of parameters that dictate what users can access and do within your product. Ideally, permissions are very granular, with each focusing on specific features.
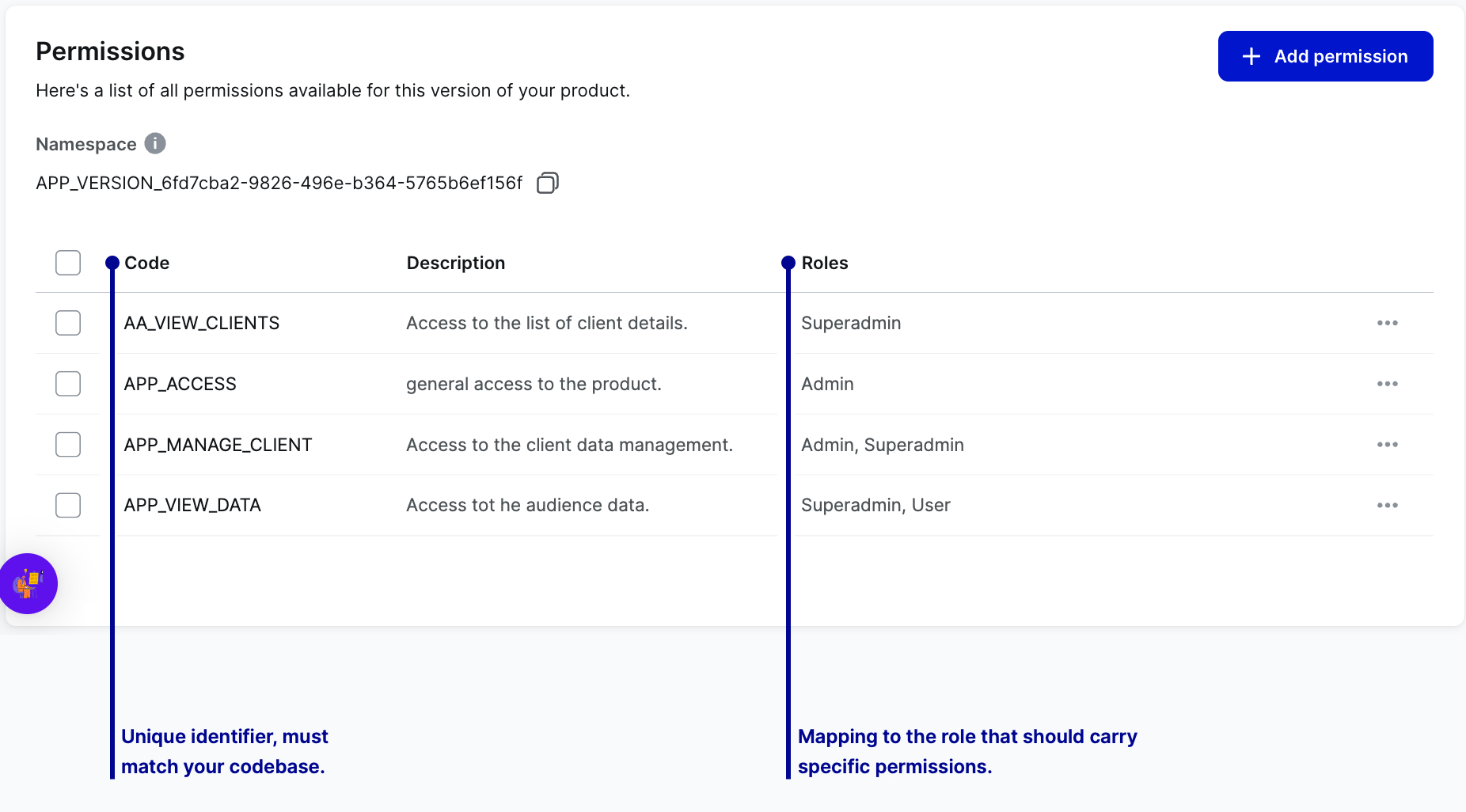
DevHub uses namespaces to mark versions that are passed to Open Authz. When you add permissions through the UI, these permissions are automatically added with a prefix under the hood. This help to avoid naming conflicts when fetching user permissions for products.
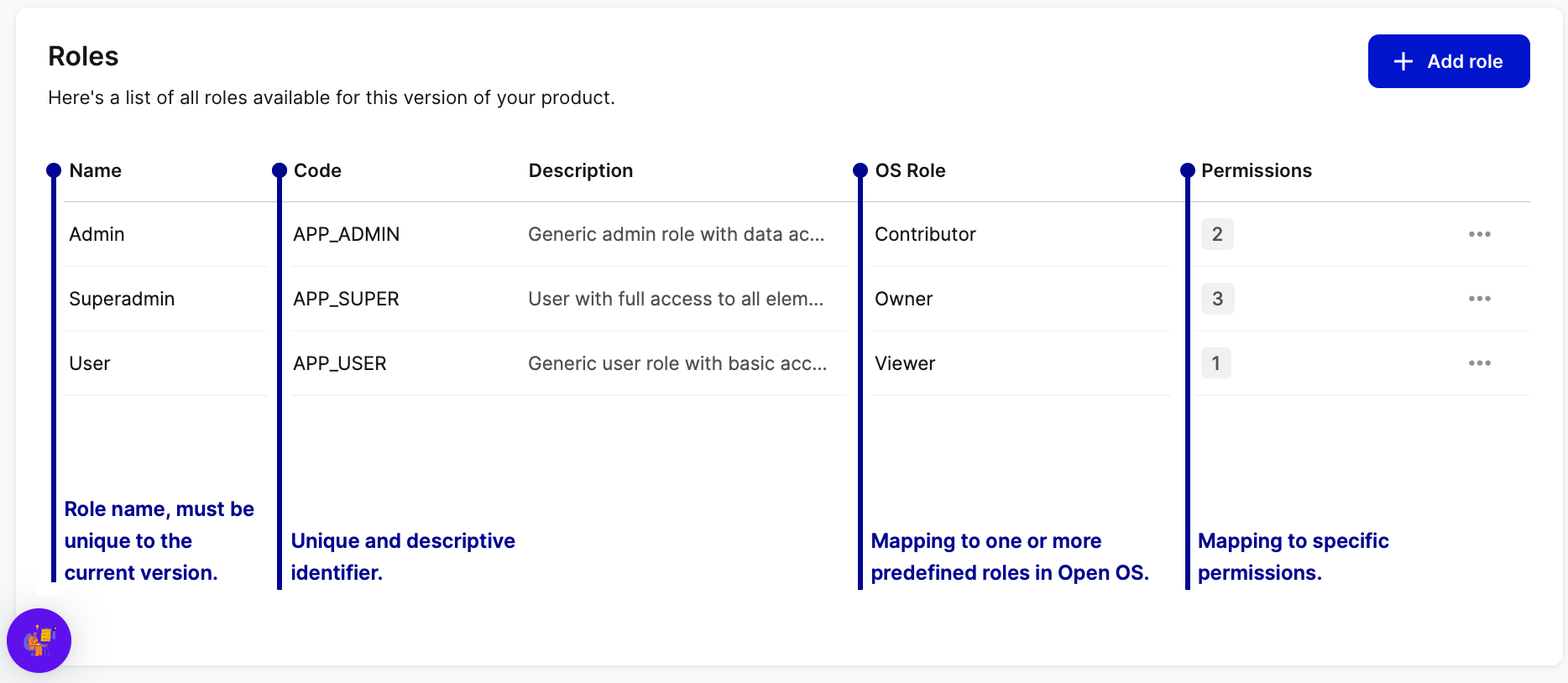
Roles
Roles are sets of permissions that operate within a predefined hierarchy. You can create roles based on the expected user structure and grant users access to specific points in your product without assigning them individual permissions.
Mapping
Mapping roles and permissions is optional in DevHub because we want to provide you with as much flexibility in product configuration as possible. However, you must map at least one role to each Open OS Meta Role before you can onboard your product to Open OS.
We require that your product has at least one role mapped to Open OS Meta Roles. This ensures that users working in Open Orchestration have the right permissions for interacting with your product:
- Viewer – can view your product within a business flow.
- Contributor – same as Viewer, and can also edit your product within a business flow.
- Owner – same as Contributor, and can also edit the project in which the specific business flow operates.
You can map many product roles to one meta role and one meta role to many product roles. For instance, you could map a Developer role to Contributor and Owner and a Project Manager role to Viewer.
After you've successfully mapped the product and meta roles, the meta roles assume the permissions associated with the product roles, and any change to the product roles updates the permissions related to the meta roles.
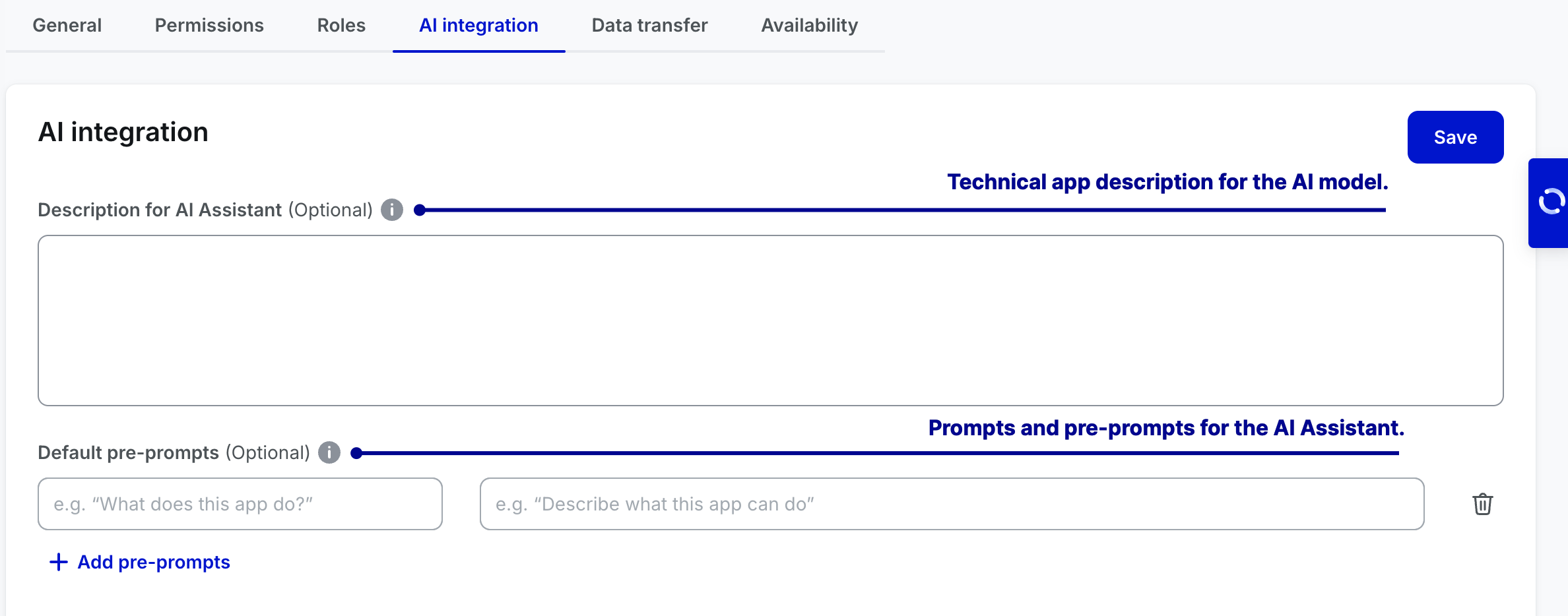
AI integration
In the AI integration tab, you can provide a technical description of your app for the AI Assistant to enable more accurate responses and interactions. You can also define default pre-prompts that the AI will use to better understand and engage with your app’s functionality.
Set up data transfer
Data transfer is currently in alpha, and its functionality is limited to demo features.
Enabling data transfer requires you to also update your product outside of DevHub.
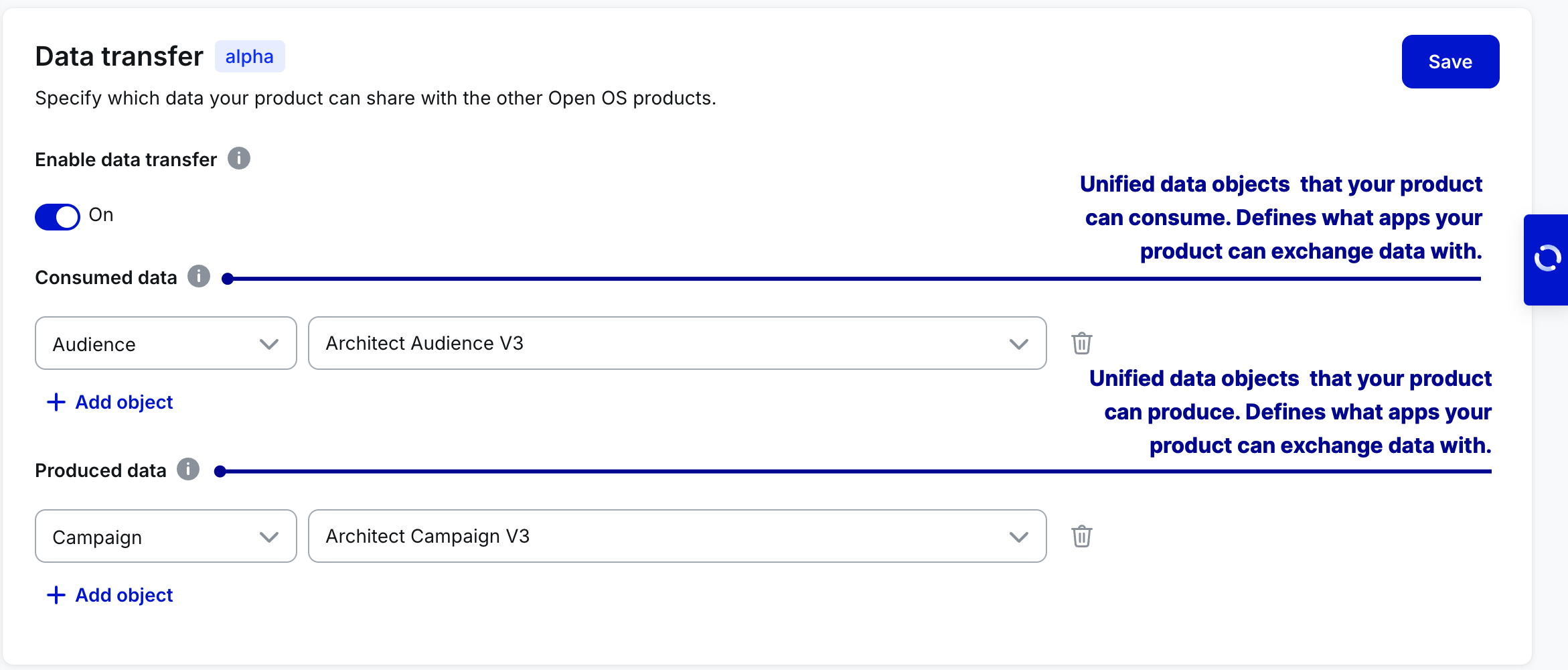
Data transfer allows your product to exchange data with other Open OS products.
Once enabled, data transfer allows you to configure your product as a producer, consumer, or both. Products exchange data in the form of predefined data objects that can have multiple schema versions, all of which you can see in the Select data object and Select schema version dropdowns.
Currently, data transfer allows products to exchange audience, campaign, and touchpoint data, and we're actively working on introducing more object types.
You can add as many object-schema pairs as you expect your product to produce and consume.
Remember that two products can exchange data only if matching object-schema pairs exist between them. To be safe, consider adding all object-schema combinations that would be reasonable for your product.
Initiate workspace availability
You can make your product available to different workspaces only after you publish it to Open Marketplace.
Availability allows you to share your product across WPP. You can make versions of your product available to all or specific workspaces under WPP Open.
Before being published to Marketplace, the app version can be activated only on the Current workspace. Once the product is published to Marketplace, it can be activated on other workspaces.
Use the search bar in the Availability tab to quickly find specific workspaces when configuring product availability in DevHub. Note that the search bar is visible only if the product is published to Marketplace and can be activated on other workspaces. Search is performed on the list of "Other workspaces" based on the workspace name.
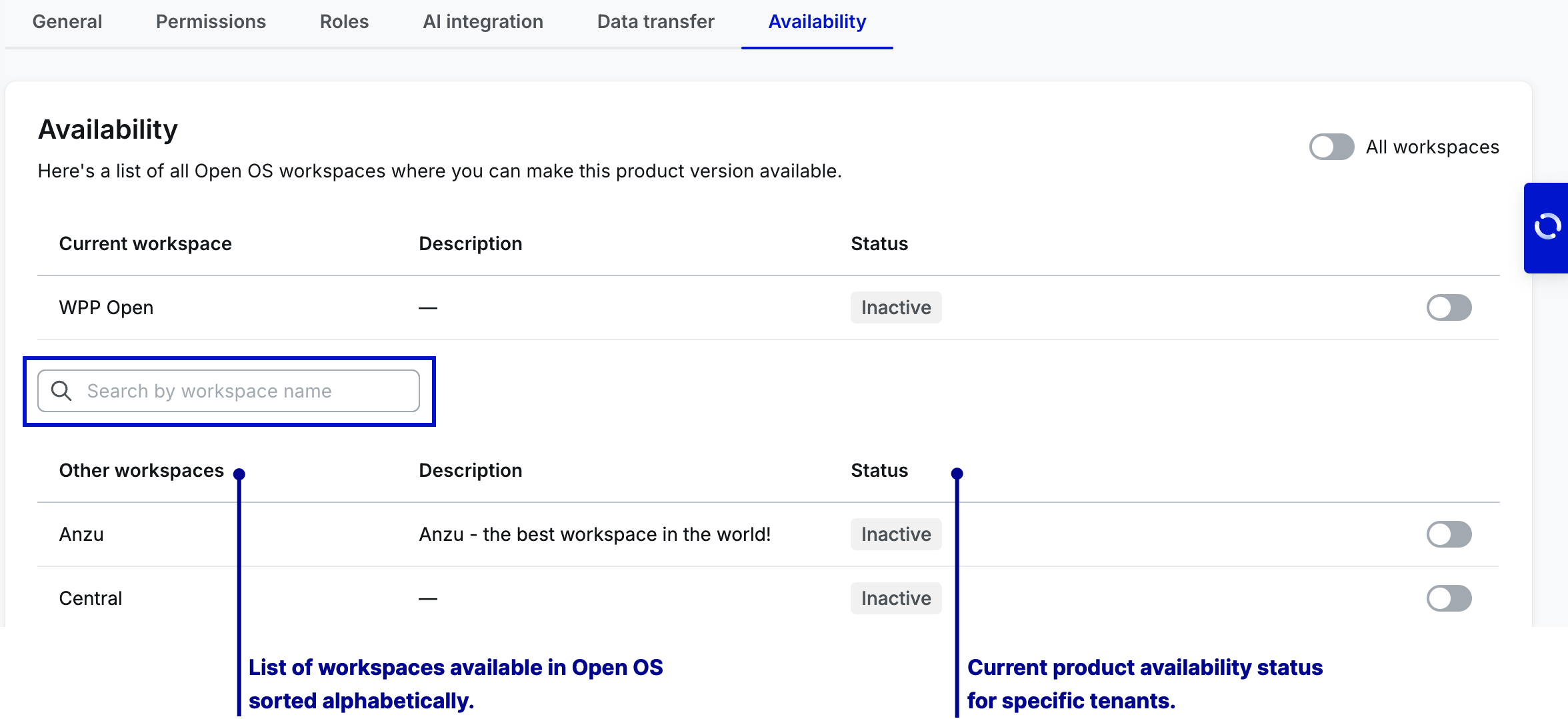
Once you activate your product for specific workspaces, the admins of those workspaces can add it to the workspace navigation. While this means that your product won't automatically become available to the workspace users, we still encourage you to be attentive when setting up product availability. Consider activation to be the final step to onboarding your product to Open OS.
WPP Open supports the global availability toggle––Activate for all workspaces.
Deactivating products may disrupt existing business flows for specific workspaces. For this reason, we recommend deactivating product versions only when necessary and communicating your timelines to the existing users.