Google analytics for apps in WPP Open
This guide outlines the standards for deploying Google Analytics (GA4) to applications in WPP Open. The primary goal of deploying GA4 on WPP Open is to enable tracking and reporting of the adoption of the system by users. Additional goals include understanding the utilisation, adoption, value generation and commercial benefits of WPP Open across different markets, agencies, clients and tools.
Implementation steps
Implementing GA4 on the web includes the following steps:
- Deploy a Google Tag Manager tag to every page on the site, or application to be tracked (App Dev Team).
- Configure a data layer to hold the data to be sent to GA4 (App Dev Team).
- Configure GTM (GA4 Team).
- Configure GA4 (GA4 Team).
This guide covers the first two steps of the process.
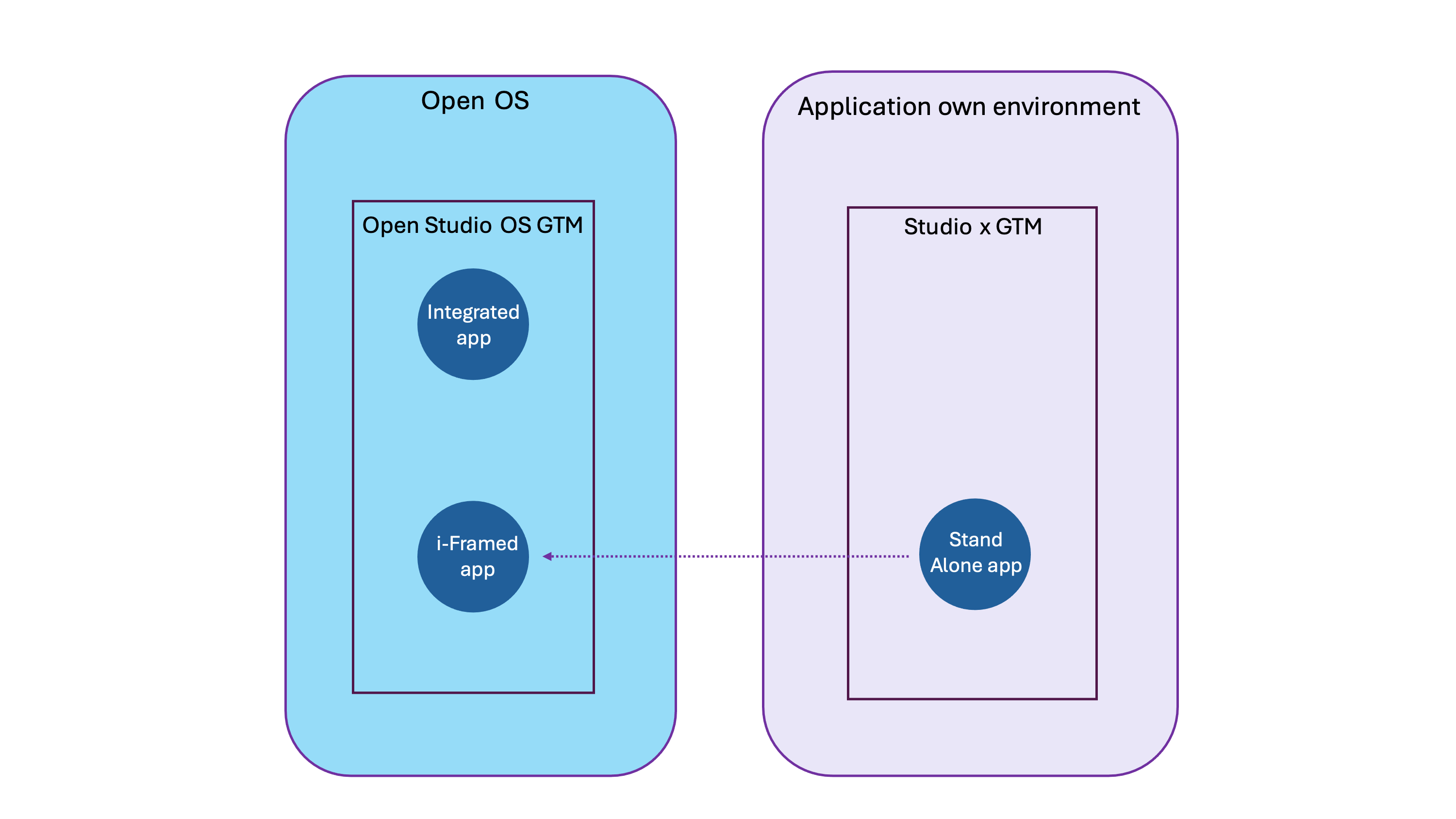
Types of WPP Open web applications
There are three ways in which applications are deployed in WPP Open:
- Integrated – these applications are built within Open OS and are integrated within the WPP Open Platform.
- i-Framed – these applications are hosted in their own environment and are accessed from WPP Open via an i-frame.
- Stand-Alone – these applications sit entirely outside of the WPP Open Platform and are accessed by users directly in their own environments.
Any application can in theory be accessed in any one of these configurations.
Integrated applications are tracked via the Core OS tag manager and data layer and do not require any additional work from the App Dev team.
Google Tag Manager (GTM)
Each Studio has been assigned a Google Tag Manager ID (GTM ID) as follows:
| Studio | GTM ID |
|---|---|
| Core OS | GTM-KSKHG4RN |
| Creative Studio | GTM-PHG7HMFL |
| Media Studio | GTM-56M5TDZ9 |
| Commerce Studio | GTM-MCJK2K3M |
| Production Studio | GTM-PVJH95C3 |
| Brand Studio | GTM-KBKFN66M |
| Experience Studio | GTM-N3D6DRHM |
| Work Management Studio | GTM-58V922NT |
| PR Studio | GTM-MCBWFVWF |
| Other Studios | GTM-MH5HD5L6 |
The code below with the correct GTM ID must be deployed on every web page to be tracked. The code
should be placed as high up in the <head> of the page as possible:
<!-- Google Tag Manager -->
<script>(function(w,d,s,l,i){w[l]=w[l]||[];w[l].push({'gtm.start':
new Date().getTime(),event:'gtm.js'});var
f=d.getElementsByTagName(s)[0],
j=d.createElement(s),dl=l!='dataLayer'?'&l='+l:'';j.async=true;j.src=
'https://www.googletagmanager.com/gtm.js?id='+i+dl;f.parentNode.insert
Before(j,f);
})(window,document,'script','wppopen','GTM-MCJK2K3M');</script>
<!-- End Google Tag Manager -->
See the official Google documentation on installing the Google Tag Manager container snippet.
The below diagram illustrates the relationship between Open OS and CO environments:
Data layer
Data layer is an object that contains all the information that you want to pass to Google Tag Manager. Rather than referencing variables, transaction information, page categories, and other important signals scattered throughout a page, Google Tag Manager is designed to easily reference information that is put in this Data layer by applying a variable called an event. This event is used within JavaScript event listeners to initiate tag firing when a user interacts with website elements such as a button.
Data object
The data object (which is the data layer object) should be deployed consistently across all pages, instances, workspaces, and any element of an application that is to be tracked.
This data object adds a layer of dimensions to all collected events, enabling segmentation of the data based on those dimensions.
The following categories of information are tracked:
- User Information: Identifies the user and their organizational context.
- Contextual Information: Provides details about the specific application, workspace, and project the user was working on.
- Action & Feature: Specifies the application, the feature used, and the task status.
- Web Analytics: Includes standard web analytics data like page details, platform, device, and browser information.
How this data can be used for tracking and analytics
- User Behaviour: Analyse how different user roles and departments interact with specific features.
- Feature Adoption: Track the usage and popularity of different features within the application.
- Performance Monitoring: Identify potential issues or bottlenecks based on task completion rates and user engagement.
- Product Development: Gather insights to inform the development of new features and improvements.
To avoid data layer clashes or overwrites, it is important to name your data layer to ‘wppopen_dataLayer’. This means that your data object won't collide with any default data layer that may be in place from another GTM container.
For reference here is a link to the official google guide: https://developers.google.com/tagplatform/tag-manager/datalayer
Data layer setup
Tags set in Google Tag Manager are commonly sending information to end points at two stages of the user website visit: immediately after the user lands on a page (Page View), or immediately after the user engages with a page (User Interaction). The data layer setup will vary accordingly.
Page View
When the data layer setup is defined as Page View setup, the data layer array code is included before the Google Tag Manager Snippet.
If the data layer code is called after the container snippet, any variables declared within will not be available for Google Tag Manager to selectively fire tags on page view.
<script>
window.wppopen_dataLayer = window.wppopen_dataLayer || [];
window.wppopen_dataLayer.push({
'event': 'sitewide',
'visitorType': 'high-value'
});
</script>
<!-- Google Tag Manager -->
//GTM container snippet would go here
<!-- End Google Tag Manager -->
User Interaction
The data layer array implementation for user interactions doesn’t require any specific setup outside a simple call to the push API immediately after the user interaction that is required to track. For example, if we want to fire a conversion tracking tag in Google Tag Manager when a user clicks the Submit button on a newsletter signup form, we could have something similar to the below:
<script>
function dataLayerTracking() {
window.wppopen_dataLayer = window.wppopen_dataLayer || [];
WPP Open GA4 Implementation
9
dataLayer.push({
'event': 'signUpNewsLetter',
'crmID': '12345'
});
}
</script>
...
<a href='#' name='newsLetter_button1'
onclick='dataLayerTracking();'>Sign Up</a>
Supported data types
Each data field in the data layer belongs to a specific type, each with its own validation rules. If any of the parameter values do not conform to the validation rules, the information sent by Google Tag Manager to the different tracking provider could be compromised.
| Data Type | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Text | Used to represent strings. | window.wppopen_dataLayer.push({'Text': 'My Text here'}); |
| Currency | Used to represent the total value of a currency. A decimal point is used as a delimiter between the whole and fractional portion. Supports up to 6 decimal places, though 2 is typical. | window.wppopen_dataLayer.push({'Currency': '1000.000001'}); |
| Boolean | Used to determine if a value is true or false. Valid values: true, false. | window.wppopen_dataLayer.push({'Boolean': true}); |
| Integer | Used to represent whole numbers. Stored as signed int64. | window.wppopen_dataLayer.push({'Integer': 25}); |
| Number | Used to represent an integer or a floating-point number. | window.wppopen_dataLayer.push({'Number': 19.6}); |
Default values
Each data field in the Data Layer must have a default value.
| Default Value | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
'unknown' | 'unknown' (type String) must be used when a value is expected to exist for a given key within a page or user interaction, but could not be retrieved. | window.wppopen_dataLayer.push({'MyVar': 'unknown'}); |
undefined | undefined (type undefined) must be used when a value is not meant to exist for a given key within a page or user interaction. | window.wppopen_dataLayer.push({'MyVar': undefined}); |
User profile data
To obtain user information and understand users and usage on WPP Open as well as Studios and Apps additional user profile data is required. We use data derived from the user’s Okta profile for this. The following variables need to be passed through in the data object (instructions for this below):
User dimensions
| Dimension Name | Description | Example Value | GA4 Parameter / User Property | Mandatory / Optional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| User ID | A unique hashed ID used to track users across sessions and platforms. | d75f4df44ef437b93309d303bbdc65e79d6db36ea3320e4d974b727a272d17c4 | user_id | Mandatory |
| User Company | WPP agency or OpCo the user belongs to. | essencemediacom | user_company | Mandatory |
| User Department | Team or department the user belongs to. | programmatic | user_department | Mandatory |
| User Job Role | The user’s job title. | digital_planner | user_job_role | Mandatory |
| User Country Code | Two-letter code for the user's country. | uk | user_country_code | Mandatory |
| User Region | Region where the user is based. | EMEA | user_region | Mandatory |
We need to pass through the correct values for the variables for each user i.e. update the profile to accommodate for the above variables.
User ID
This should be the hashed email address.
For normalisation:
- Remove leading or trailing whitespaces.
- Convert the text to lowercase. For hash: Use hex SHA256.
This site can be used to validate the output: https://emn178.github.io/online-tools/sha256.html
The table below lists more information about the customer data variables that you can define. Note that all data should be passed as ‘String’ type variables.
Apps in Open
Populate the datalayer with the data passed to the application from Open’s context object:
| Context Key | Data Layer Object |
|---|---|
userDetails->email (pre hash) | user_id (hashed) |
userDetails->company | user_company |
userDetails->countryAlpha2Code | user_country_code |
userDetails->department | user_department |
userDetails->jobTitle | user_job_role |
userDetails->geoRegion | user_region |
Standalone apps outside of Open
It is vital we accurately capture the identity of the user so we can attribute user to the correct OpCo, Country and Job Role.
To allow for consistency in this regard, we use Okta and its Okta Object, which provides a common way for all applications (that use Okta) to send consistent data points for that user for use within GA4.
Okta object to Data layer mapping
| Okta Object | Data Layer Object |
|---|---|
email (pre hash) | user_id (hashed) |
company | user_company |
countryCode | user_country_code |
department | user_department |
title | user_job_role |
geoRegion | user_region |
Mandatory custom events
There are three events that are a required for all applications. Firstly, there is an event (user_login) to capture logins. Parameters for this event come from the OKTA Object. The second event (app_launch) is fired on the launch of an application. The third is page_view for when the page loads in the browser. If your application is a SPA then there is a 4th Mandatory Event for virtual_page_views to cope with state changes that don’t reload the page.
User login event
Apps launched via Open should not send the user_login event, but if they can also be launched
standalone, then they should only send the user_login event when launched standalone.
Setup
The data object should be implemented following the Page View setup spec above as typically the user should gain access to the application via the Okta Verification process before seeing a home page. Note that Login still would be required if a user previously followed the Okta Verification Process and was not prompted on entry to the Application. Please see the section about WPP User Meta Data for more detail.
Code example
{
"event": "user_login",
"user_id":
"d75f4df44ef437b93309d303bbbdc65e79d6db36ea3320e4d974b727a272d17c4"
,
"user_company": "Choreograph",
"user_country": "GB",
"user_department": "Analytics",
"user_job_role": "Lead Technology Consultant – Digital
Analytics",
"user_region": "EMEA",
}
| Data Layer Object | Mandatory / Optional |
|---|---|
user_id (hashed) | Mandatory |
user_company | Mandatory |
user_country_code | Mandatory |
user_department | Mandatory |
user_job_role | Mandatory |
user_region | Mandatory |
Page_View
Setup
The data object should be implemented following the Page View setup. So, when a page is loaded in the browser we send the following data object when the dataLayer items are available, if items are not applicable then please do set as undefined.
Code example
{
"event": "page_view",
"user_id":
"d75f4df44ef437b93309d303bbbdc65e79d6db36ea3320e4d974b727a272d17c4",
"workspace_market": "EMEA",
"workspace_industry": "Food and Drink",
"workspace_brand": "TCCC",
"workspace_client": "The Coca Cola Company",
"workspace_region": "APAC",
"workspace_custom": "TCCC",
"context_type": "os",
"tenant_name": "WPP Open",
}
Datalayer key explanations
| DataLayer Key Name | Description | Mandatory / Optional |
|---|---|---|
user_id | Mandatory | |
workspace_market | The market name from hierarchy->mapping with type='Market', or undefined. | Mandatory |
workspace_industry | The industry name from hierarchy->mapping with type='Industry', or undefined. | Mandatory |
workspace_brand | The brand name from hierarchy->mapping with type='Brand', or undefined. | Mandatory |
workspace_client | The client name from hierarchy->mapping with type='Client', or undefined. | Mandatory |
workspace_region | The region name from hierarchy->mapping with type='Region', or undefined. | Mandatory |
workspace_custom | The custom name from hierarchy->mapping with type='custom', or undefined. | Mandatory |
context_type | Value must be either "os" or "standalone". | Mandatory |
tenant_name | From context object (tenant->name), otherwise undefined. | Mandatory |
Virtual_Page_View
Setup
In a single-page application, when triggering a new page_view due to a screen change without reloading the browser page, the following approach should be used.
The pageUrl, previousUrl, and pageTitle parameters must be dynamically updated to reflect the current screen's URL and title. If the URL includes hash fragments (#) or query parameters (?), these should also be included.
Code example
{
"event": "virtual_page_view",
"user_id":
"d75f4df44ef437b93309d303bbbdc65e79d6db36ea3320e4d974b727a272d17c4",
"pageUrl": "https://www.mywebsite.com/something/?page#contact-us",
"pageTitle": "Contact us' //some arbitrary name for the page/state",
"previousUrl": "https://www.mywebsite.com/something-else/",
"workspace_market": "EMEA",
"workspace_industry": "Food and Drink",
"workspace_brand": "TCCC",
"workspace_client": "The Coca Cola Company",
"workspace_region": "APAC",
"workspace_custom": "TCCC",
"context_type": "os",
"project": "project X",
"tenant_name": "WPP Open",
}
Datalayer key explanations
| DataLayer Key Name | Description | Mandatory / Optional |
|---|---|---|
user_id | Mandatory | |
pageUrl | Current URL | Mandatory |
pageTitle | Current Page Title | Mandatory |
previousUrl | Previous URL | Mandatory |
workspace_market | The market name from hierarchy->mapping with type='Market', or undefined. | Mandatory |
workspace_industry | The industry name from hierarchy->mapping with type='Industry', or undefined. | Mandatory |
workspace_brand | The brand name from hierarchy->mapping with type='Brand', or undefined. | Mandatory |
workspace_client | The client name from hierarchy->mapping with type='Client', or undefined. | Mandatory |
workspace_region | The region name from hierarchy->mapping with type='Region', or undefined. | Mandatory |
workspace_custom | The custom name from hierarchy->mapping with type='custom', or undefined. | Mandatory |
context_type | Value must be either "os" or "standalone". | Mandatory |
project | From context object (project->name), otherwise undefined. | Mandatory |
tenant_name | From context object (tenant->name), otherwise undefined. | Mandatory |
Application launch event
Setup
The data object should be implemented following the Page View setup. Typically, a user will launch an application from a click.
Code example
{
"event": "app_launch",
"user_id":
"d75f4df44ef437b93309d303bbbdc65e79d6db36ea3320e4d974b727a272d17c4",
"application_id": "0a1c0520-8c67-1590-818c-68fa74bb004b",
"application_instance_id": "0a1c0520-8c67-1590-818c-68fa74bb004b",
"product_type": "NO_CODE_APPLICATION",
"nocode_apptype": "EMBEDDED_LINK",
"workspace_market": "EMEA",
"workspace_industry": "Food and Drink",
"workspace_brand": "TCCC",
"workspace_client": "The Coca Cola Company",
"workspace_region": "APAC",
"workspace_custom": "TCCC",
"context_type": "os",
"product_name": "creative-studio",
"product_category": "Media",
"product_subcategory": "Planning",
"tenant_name": "WPP Open",
}
DataLayer key explanations
| DataLayer Key Name | Description | Mandatory / Optional |
|---|---|---|
user_id | Mandatory | |
application_id | Taken from context object: appInstance->devhubAppId | Mandatory |
application_instance_id | Taken from context object: appInstance->id | Mandatory |
product_type | Taken from context object: appInstance->devhubMetadata->productType | Mandatory |
nocode_apptype | Taken from context object: appInstance->devhubMetadata->noCodeAppType, or undefined | Mandatory |
workspace_market | The market name from hierarchy->mapping with type='Market', or undefined | Mandatory |
workspace_industry | The industry name from hierarchy->mapping with type='Industry', or undefined | Mandatory |
workspace_brand | The brand name from hierarchy->mapping with type='Brand', or undefined | Mandatory |
workspace_client | The client name from hierarchy->mapping with type='Client', or undefined | Mandatory |
workspace_region | The region name from hierarchy->mapping with type='Region', or undefined | Mandatory |
workspace_custom | The custom name from hierarchy->mapping with type='custom', or undefined | Mandatory |
context_type | Value must be either "os" or "standalone" | Mandatory |
product_name | The name of the product. Ensure the same name is used whether the app is registered multiple times in Open or also runs standalone | Mandatory |
product_category | A meaningful one-word value that reflects the general product area of the application, e.g. Media, PR | Mandatory |
product_subcategory | A meaningful one/two-word value that reflects the activity or sub-area the application supports, e.g. planning, production, strategy, etc. | Mandatory |
project | If context object contains project key then populate with project->name, otherwise undefined | Mandatory |
tenant_name | From context object (tenant->name), otherwise undefined | Mandatory |
Work with the Open OS team to see how your application can receive data from Open OS for context around Workspaces, Projects, etc. For more details, see the Open OS Context guide.
Optional custom events
The following custom events have been defined and are available for more granular tracking of user activity. Parameters that are not required may be omitted from the data layer or set to ‘undefined’. If additional events or parameters are required, they will first have to be requested and enabled in GA4 by the GA4 team.
Action interaction events
Complete DataLayer key reference
| DataLayer Key Name | Description | Mandatory / Optional |
|---|---|---|
user_id | Mandatory | |
application_id | Taken from context object: appInstance->devhubAppId | Mandatory |
application_instance_id | Taken from context object: appInstance->Id | Mandatory |
product_type | Taken from context object: appInstance->devhubMetadata->productType | Mandatory |
nocode_apptype | Taken from context object: appInstance->devhubMetadata->noCodeAppType, or undefined | Mandatory |
workspace_market | The market name from hierarchy->mapping with type='Market', or undefined | Mandatory |
workspace_industry | The industry name from hierarchy->mapping with type='Industry', or undefined | Mandatory |
workspace_brand | The brand name from hierarchy->mapping with type='Brand', or undefined | Mandatory |
workspace_client | The client name from hierarchy->mapping with type='Client', or undefined | Mandatory |
workspace_region | The region name from hierarchy->mapping with type='Region', or undefined | Mandatory |
workspace_custom | The custom name from hierarchy->mapping with type='custom', or undefined | Mandatory |
context_type | Value must be either "os" or "standalone" | Mandatory |
product_name | The name of the product; should remain consistent even if app is registered multiple times or used standalone | Mandatory |
product_category | A one-word value reflecting the general product area, e.g., Media, PR | Mandatory |
product_subcategory | A one- or two-word value reflecting the sub-area or activity the app supports, e.g., planning, strategy, production | Mandatory |
project | If context object contains project, populate with project->name, otherwise undefined | Mandatory |
tenant_name | From context object tenant->name, otherwise undefined | Mandatory |
click_object | Can be: 'Image', 'Button', 'Link', 'Icon' | Mandatory |
click_page_path | Example: {{page_path}} | Mandatory |
click_text | Example: {{image_text}}, {{alt_text}}, {{button_text}}, {{link_text}} | Mandatory |
click_target_path | Example: {{url_target_path}} | Optional |
Code example
window.wppopen_dataLayer.push({
"event": "click",
"user_id": "d75f4df44ef437b93309d303bbbdc65e79d6db36ea3320e4d974b727a272d17c4",
"application_id": "0a1c0520-8c67-1590-818c-68fa74bb004b",
"application_instance_id": "0a1c0520-8c67-1590-818c-68fa74bb004b",
"product_type": "NO_CODE_APPLICATION",
"nocode_apptype": "EMBEDDED_LINK",
"workspace_market": "EMEA",
"workspace_industry": "Food and Drink",
"workspace_brand": "TCCC",
"workspace_client": "The Coca Cola Company",
"workspace_region": "APAC",
"workspace_custom": "TCCC",
"context_type": "os",
"product_name": "creative-studio",
"product_category": "Media",
"product_subcategory": "Planning",
"project": "Project Xmas",
"tenant_name": "WPP Open",
"click_object": "button",
"click_page_path": "/hubs/",
"click_text": "Request Growth Support",
"click_target_path": undefined
});
Feature function events
Use the feature function event to capture the principal features of your product that a user is interacting
with. For example, a user may launch the app and navigate to an asset management page and proceed to
upload a new asset. In this scenario, a feature_activate event should be sent to track the usage of the
asset management feature (i.e. the feature_category) to upload assets (feature_context). The name of each asset can be included using the feature_freeform_[n] keys. Up to 10
feature_freeform_ keys can be added as needed.
Carefully consider which features to send feature_activate events for. These should not be so granular
that it becomes unclear what user’s purpose is.
The feature_complete event may be used to indicate something as completed, e.g. the upload of assets
is finished, AI image or text generation has completed, etc. It is not necessary to send a
feature_complete for each feature_activate. Consider using this if it may be useful to understand data
about the outcome of using a particular feature, e.g. the size of an audience for a particular audience
definition.
The feature_settings event may be used to capture information about how a user may have adjusted a
particular feature, e.g. applying filtering, particularly if it has a strong bearing on how the feature may be
feature_settings if the adjustment would result in a feature_activate event being sent.
Feature event parameters
| Event name | Parameter | Example value | Mandatory / Optional |
|---|---|---|---|
feature_activate | feature_category | AI Image | Mandatory |
feature_context | Generate Image | Mandatory | |
feature_freeform_1 | {{model_used}} | Optional | |
feature_freeform_2 | {{images_generated}} | Optional | |
feature_complete | feature_category | AI Image | Mandatory |
feature_context | Remove Element | Mandatory | |
feature_freeform_1 | {{model_used}} | Optional | |
feature_freeform_2 | {{images_generated}} | Optional | |
feature_settings | feature_category | AI Image | Mandatory |
feature_context | Change Model | Mandatory | |
feature_freeform_1 | Optional | ||
feature_freeform_2 | {{images_generated}} | Optional |
Code example
window.wppopen_dataLayer.push ({
"event": "feature_activate",
"user_id":
"d75f4df44ef437b93309d303bbbdc65e79d6db36ea3320e4d974b727a272d17c4",
"applicationwide": "0a1c0520-8c67-1590-818c-68fa74bb004b",
"application_instance_id": "0a1c0520-8c67-1590-818c-68fa74bb004b",
"product_type": "NATIVE_APPLICATION",
"nocode_apptype": "",
"workspace_market": "EMEA", //context object
"workspace_industry": "Food and Drink", //context object
"workspace_brand": "TCCC", //context object
"workspace_client": "The Coca Cola Company", //context object
"workspace_region": "APAC", //context object
"workspace_custom": "TCCC", //context object
"context_type": "os",
"product_name": "creative-studio",
"product_category": "Media",
"product_subcategory": "Planning",
"project": "Project Xmas", //context object
"tenant_name": "WPP Open", //context object
"feature_category': 'AI Image",
WPP Open GA4 Implementation
29
"feature_context': 'generate image",
"feature_freeform_1': 'Gemini",
"feature_freeform_2': 20
});